Font Size:
Sublimation Transfer Paper Structure and Related Coating Chemicals
Applications and Prospects of Sublimation Transfer Paper Sublimation transfer paper finds wide applications in mass-producing textiles like T-shirts, curtains, bedding, etc. Additionally, it is utilized in ceramics, metals, home accessories, and personalized commemorative products. Textiles constitute the primary application sector, as illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Thermal sublimation transfer process and application The rapid development across various industries in China, particularly the evolving trends in the clothing sector, has propelled the growth of sublimation transfer paper. Figure 2 depicts the variation in thermal transfer paper output in China from 2011 to 2021

Figure 2: Variation of thermal transfer paper output in China during 2011-2021
Sublimation Heat Transfer Paper Sublimation transfer paper typically comprises three components: sublimation transfer paper base paper, pre-coating layer, and transfer layer, as depicted in Figure 3. To achieve high-quality printing and transfer effects, the sublimation transfer base paper necessitates specific attributes including minimal filler, high whiteness, smoothness of about 30s, uniformity, appropriate tightness, and low air permeability. Additionally, high tensile index, tear index, and heat resistance are required to prevent paper breakage.
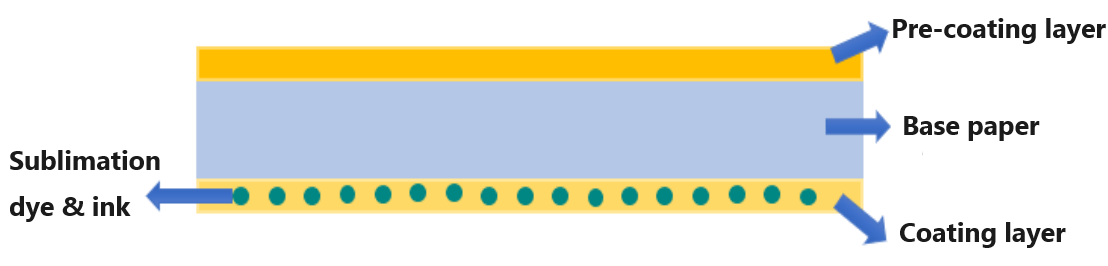
Figure 3: Structure of thermal sublimation transfer paper
2.1 Pre-Coating Layer The pre-coating layer involves surface sizing of pulp, offering various advantages such as improving surface strength, reducing lint and powder issues, and enhancing transfer performance. The optimal formula for pre-coating sublimation transfer base paper includes a specific ratio of light calcium carbonate to china clay, adhesive amount, PVA to latex ratio, and water-repellent agent quantity.
2.2 Coating Layer The coating layer, also known as the transfer layer, aims to provide excellent ink absorption while preventing excessive ink absorption into paper fibers. It controls ink dot increase and facilitates the formation of high-quality images and text. The coating comprises adhesives, pigments, and functional additives.
(1) Adhesive The adhesive's primary role is to bond pigments to each other and to the base paper while filling gaps between particles. Ideal adhesives exhibit stable chemical and physical properties, good bonding ability and water retention, solubility in water, compatibility with other components, and are non-toxic and odorless.
(2) Pigments Pigments, the main component in coatings, must possess desirable chemical stability, high refractive index, dispersion, low density, and compatibility with other components. Pigments are divided into main, special, and auxiliary categories based on dosage and desired performance.
(3) Functional Additives Functional additives are incorporated to improve coating performance, ensure quality, and mitigate external factors' impact. These additives include dispersants, defoaming agents, water retaining agents, rheology regulators, water repellents, and bactericides.
The sublimation transfer paper produced by Qingdao JIERUIXIN Machinery and Technology CO.,Ltd's coating equipment boasts a transfer rate exceeding 96%. It is suitable for chemical fiber items or textile products with less than 30% cotton content. For equipment solutions and chemical preparation inquiries or paper purchases, please feel free to contact us.
Commonly used chemical materials for pigment coating
An alcohol-proof thermal paper with long time image retention- the coating method
Carbonless paper coating chemicals components
2024-02-04The Impact of Stiffness and Density on the Quality of Coated Paper
2024-02-04Quality index of coated base paper
2024-02-04Explore the development of the thermal paper market since 2023: Trends, challenges and opportunities
2024-02-04Unveiling the Divergence: Boiler vs Steam Generator in Paper Drying
2024-02-04What is the thermal paper coating machine line?
2024-02-04Why does the thermal paper coating machine request calender?
2024-02-04Carbonless paper coating chemicals components
2024-02-04The Impact of Stiffness and Density on the Quality of Coated Paper
2024-02-04Quality index of coated base paper
2024-02-04